Before completing Section F complete Section G first (unless you are not required to complete Section G). See Requirements To Complete Section G , later, to determine your requirement. Check “Yes” if any of the QREs on line 48 are following the ASC 730 Directive. Partnerships and S corporations report the above credits on line 29. Also, estates and trusts that can allocate the source credit to beneficiaries report the above credits on line 29. All other filers figuring a separate credit on earlier lines also report the above credits on line 29.
Non-Qualifying Activities
“Qualified research” means research for which expenses may be treated as section 174 expenses. This research, often referred to as the “four-part test”, must be undertaken for discovering information that is technological in nature, what is r&d tax credit and its application must be intended for use in developing a new or improved business component of the taxpayer. In addition, substantially all of the activities of the research must be elements of a process of experimentation relating to a new or improved function, performance, reliability, or quality. These tests to determine qualified research must be applied separately with respect to each business component of the taxpayer. The taxpayer must intend to apply the information being discovered to develop a new or improved business component of the taxpayer. A business component is any product, process, computer software, technique, formula, or invention, which is to be held for sale, lease, license, or used in a trade or business of the taxpayer.
Qualified Research
Any other statement or report, such as a review statement or a compilation report that is not subject to a full audit is not a certified audited statement. 1 Subsequent section references are to the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended and in effect during the tax years Accounting Errors at issue and to the Treasury regulations promulgated thereunder, unless otherwise specified. Partner with us and watch your business thrive through strategic tax incentives.
What businesses need to know about the new Form 6765
- Diana Miller-Lloyd, 44, who currently lives in Jacksonville, FL, pleaded guilty in Hartford federal court to aiding in the preparation of false tax returns.
- For example, designing a new surgical robot, a more sensitive MRI machine component, or a wearable health monitoring device.
- Amending returns may provide cash refunds but may also require pass-through entity owners to amend their individual returns.
- Foreign R&D expenses, however, remain subject to 15-year amortization, preserving a distinction that aligns with policy goals related to domestic innovation.
- The Treasury Department and the IRS believe that the inclusion of a separate process of experimentation requirement in the statute makes this proposition clear.
- Tilstone strongly recommends partnering with a CPA or accountant to make sure you’re eligible for this credit.
Many companies find that after setting up a system for capturing qualifying costs (essentially creating an “R&D culture” of documentation), the ongoing compliance becomes part of the routine. And since innovation is a key part of growth, the credit effectively becomes a self-reinforcing cycle – you save money, which can be reinvested into more R&D. Identify and gather support for the credit to which you’re legally entitled. Report the credit on a timely-filed (including extensions) federal tax return using Form 6765. If the entity reporting the credit is a pass-through, the partner or shareholder will report their share of credits via Form K-1 on their 1040 returns to monetize the credit. Businesses that qualify for the R&D tax credit must encounter a problem with a high degree of technical uncertainty and try to solve it using their own procedures.
Guidance/Process for including the five items of information on amended returns
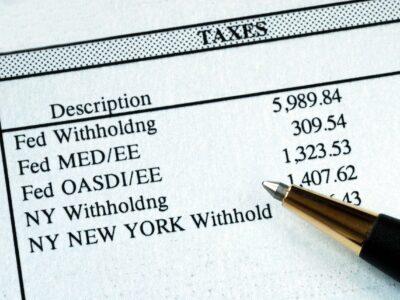
- As an example, a company that employs 100 employees with an average salary of $95,000 per person would pay approximately $589,000 in Social Security payroll taxes and $137,750 in Medicare payroll taxes.
- If you include any new categories or recharacterized any categories of expenses in the current year compared to the base year(s), those expenses must be included and adjusted in any of the base years when computing the credit.
- These FAQs do not provide a complete analysis of all relevant law under IRC 41 or 174.
- Any exemption would not apply to amended returns for the research credit.
- If the answer to either question is no, then the research is treated as funded.
- Enter the total amount of in-house wage QREs incurred by persons engaged in direct support of qualified research activities for each 80%/Top 50 and the aggregate business components.
Companies investing in R&D should consider claiming RDAs https://www.bookstime.com/ on capital investments to avoid missing potential tax benefits. However, claims for RDAs on capital expenditures are often significantly lower than those for revenue expenditures. The regulations clarify that merely demonstrating that uncertainty has been eliminated is insufficient to satisfy the process of experimentation test. Focus upon developing facts necessary to determine whether the taxpayer’s activities meet these requirements and the core elements.
How to elect the payroll tax credit – Qualified small business employer filing under its own EIN
The R&D Tax Credit is a valuable incentive that encourages innovation by providing significant financial benefits to businesses investing in research and development. Companies of all sizes should consider exploring their eligibility to take advantage of this credit, which can reduce tax liabilities and support growth. The research activity must be related to developing or improving the functionality, quality, reliability, or performance of a business component. A “business component” is broadly defined and includes any product, process, software, technique, formula, or invention. The permitted purpose criterion is met if the goal of the activity is to create something new or improve something that exists, adding value to the business. If this happens, you need to understand the benefits of each so you can make an informed decision on which credit to take.